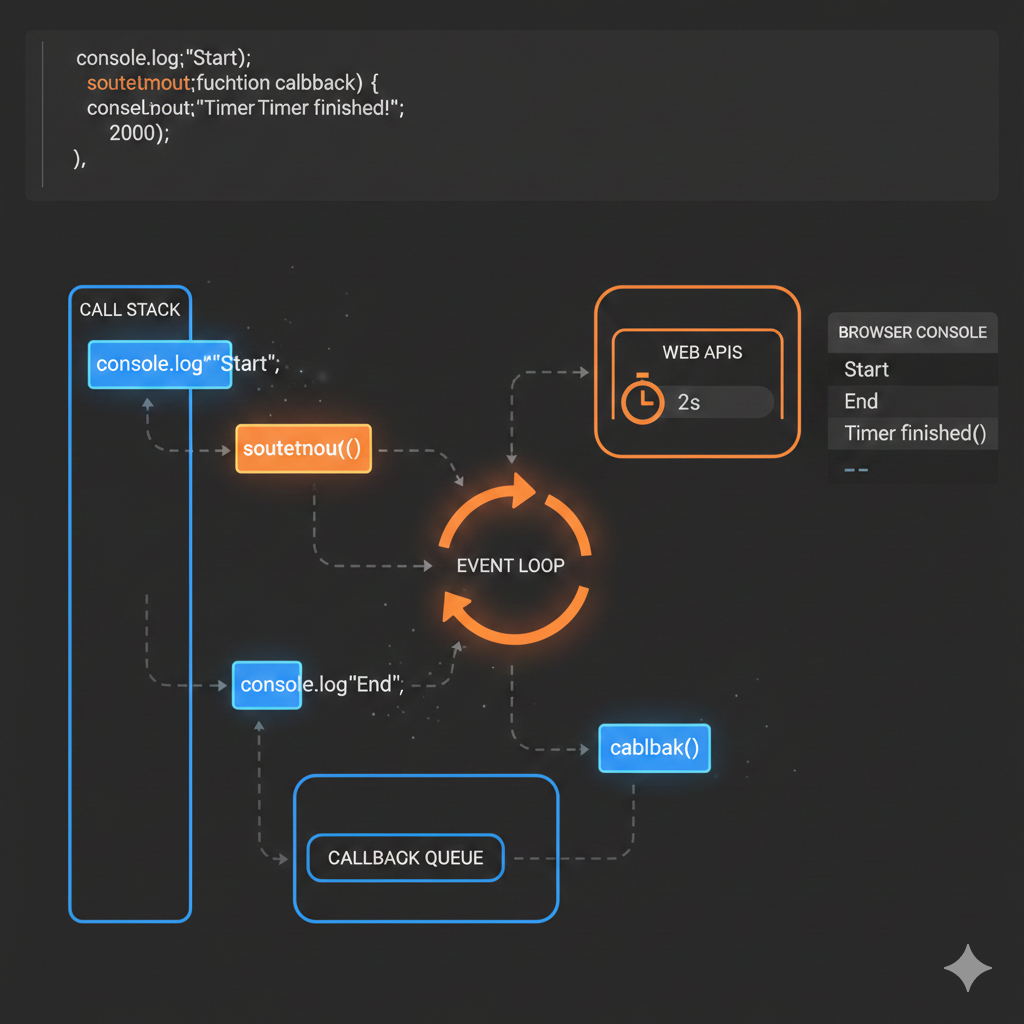
Welcome to the world of NestJS!
If you’re looking to build efficient, scalable, and maintainable server-side applications, you’ve come to the right place.
NestJS is a progressive Node.js framework heavily inspired by Angular, providing an out-of-the-box architecture for enterprise-grade backends.
In this tutorial, we’ll walk through the basics of setting up a NestJS project and creating your first API endpoint.
Why Choose NestJS?
-
TypeScript by Default: Brings static typing and improved code quality.
-
Modular Architecture: Keeps your application organized as it grows.
-
Powerful CLI: Speeds up development by generating boilerplate code.
-
Scalability: Designed specifically for large-scale applications.
Prerequisites
Make sure you have the following installed:
-
Node.js (LTS version recommended)
-
npm (comes with Node)
Step 1: Install the NestJS CLI
The CLI allows you to generate modules, controllers, and services with simple commands. Open your terminal and run:
npm i -g @nestjs/cli
Step 2: Create a New Project
Navigate to your desired folder and run:
nest new my-nest-app
Select npm as your package manager. Once finished, move into the project:
cd my-nest-app
Step 3: Run the Application
To start the development server with “watch mode” (which restarts whenever you save a file), run:
npm run start:dev
Your app is now running at http://localhost:3000. You should see “Hello World!” in your browser.
Step 4: Building a “To-Do” API
Let’s build a functional API. We will generate a Module, a Controller (to handle requests), and a Service (to handle logic).
1. Generate the Files
Run these commands in your terminal:
nest g module todos
nest g controller todos
nest g service todos
2. Implement the Service
Open src/todos/todos.service.ts and replace the code with this logic to manage a simple array:
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
interface Todo {
id: number;
title: string;
completed: boolean;
}
@Injectable()
export class TodosService {
private todos: Todo[] = [];
private nextId = 1;
findAll(): Todo[] {
return this.todos;
}
create(title: string): Todo {
const newTodo = { id: this.nextId++, title, completed: false };
this.todos.push(newTodo);
return newTodo;
}
findOne(id: number): Todo {
return this.todos.find(todo => todo.id === id);
}
}
3. Implement the Controller
Open src/todos/todos.controller.ts and update it to handle HTTP requests:
import { Controller, Get, Post, Body, Param } from '@nestjs/common';
import { TodosService } from './todos.service';
@Controller('todos')
export class TodosController {
constructor(private readonly todosService: TodosService) {}
@Get()
getAll() {
return this.todosService.findAll();
}
@Post()
create(@Body('title') title: string) {
return this.todosService.create(title);
}
@Get(':id')
getOne(@Param('id') id: string) {
return this.todosService.findOne(+id);
}
}
Step 5: Test Your API
You can use a tool like Postman or Insomnia to test your new endpoints:
-
POST
http://localhost:3000/todoswith a JSON body:{"title": "Learn NestJS"}. -
GET
http://localhost:3000/todosto see your list.
Conclusion
You’ve just built a working REST API with NestJS!
From here, you can explore database integration with TypeORM, add Validation Pipes, or implement JWT Authentication.
Useful links below:
Let me & my team build you a money making website/blog for your business https://bit.ly/tnrwebsite_service
Get Bluehost hosting for as little as $1.99/month (save 75%)…https://bit.ly/3C1fZd2
Best email marketing automation solution on the market! http://www.aweber.com/?373860
Build high converting sales funnels with a few simple clicks of your mouse! https://bit.ly/484YV29
Join my Patreon for one-on-one coaching and help with your coding…https://www.patreon.com/c/TyronneRatcliff
Buy me a coffee